|
Solenoid Valve Specifications and Dimensions: 2V130-500 Series
|
Valve Model |
2V130-3/8 |
2V130-1/2 |
2V130-3/4 |
2V250-1 |
|
Valve Type
|
2 Way Normally
Closed (NC) |
|
Action |
Pilot
Lift Diaphragm |
|
Cv (Orifice) |
|
|
|
|
|
Operating
Pressure |
5 to 115 PSI , 5 to 150
PSI (with high power coil) |
|
Operating
Temperature |
14
to 176 °F
(-10 TO 80
°C);
5 to 248 °F
(-15 TO 120
°C) (with Viton
Seal) |
|
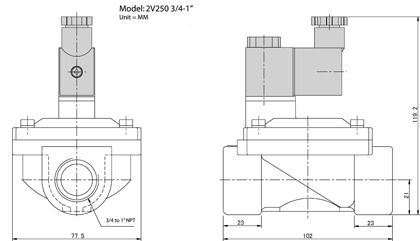
Port Size (NPT) |
3/8 |
1/2 |
3/4 |
1 |
|
Body Materials |
Brass |
|
Seal Materials:
|
NBR (Option: Viton) |
|
Coil Protection
Insulation Class |
F Class IP65,
Option: Explosion Proof Coil |
|
Coil Duty
|
100% ED
|
|
Coil Power
|
|
|
Electrical
Connections |
DIN |
|
Service |
Air, Gas,
Liquid, Vacuum, Steam (with Viton seal) |
|
ALL Standard valves are supplied with CONTINUOUS DUTY COILS
of the proper class of insulation for the service indicated on the valve.
The coil temperature may become hot after being energized for extended
periods, but it is normal. Smoke or burning odor indicates excessive coil
temperature and should disconnect the power to the coil immediately.
VOLTAGES: Standard: 12-24V DC and 24-110-220-230V/50-60 Hz AC. Voltage
tolerances: +10% –5% for DC, +10%-15% for AC; .
SERVICE LIFE: The service life of the solenoid valve depends on the
operating conditions such as pressure, temperature, type of medium and the
voltage. |
|
Electrical Coil Connections |
|
For DIN Coil |
To connect DIN coil:
1. Remove the Philip screw from the plastic housing and unplug it from the
DIN coil.
2. From the screw opening, push the terminal block out from the plastic
housing.
3. Note the 1, 2 and ground markings on underside of DIN enclosure.
4. For DC DIN Coil, Connect 1 to Positive, 2 to Negative.
5. For AC DIN Coil, connect 1 to HOT wire, 2 to Neutral wire, and if
required connect ground to ground wire. |
|
For Grommet Coil |
To connect Grommet coil:
1. For DC Coil, connect one of the two wires to Positive, and the
other wire to Negative.
2. For AC Coil, connect one of the two wires to HOT wire, and the other wire
to neutral wire. |
|
2V130-250 Series 2/2 Pilot Operated
Diaphragm Solenoid Valve NC
To open: when the solenoid valve is energized, a magnetic field from the
coil attracts the plunger covering the pilot orifice to lift off,
causing system pressure (holding the diaphragm closed) to drop. As
system pressure on the top of the diaphragm is reduced, full system
pressure on the other side of the diaphragm acts to lift the
diaphragm away from the main orifice, which allows media flow through
the valve. Since the bleed orifice is dimensionally smaller than the pilot
orifice, the system pressure cannot rebuild on the top of the
diaphragm as long as the pilot orifice remains open.
To close:
when the solenoid valve is de-energized, it releases its hold on the plunger,
allowing the plunger spring forces
the plunger to covers the main orifice. The system pressure builds up
on the top of the diaphragm through the bleed orifice, forcing the
diaphragm down until it covers the main orifice and stops media flow
through the valve



|
|

|
 |
|









